
Fast, affordable Internet access for all.
Community Anchor Institutions, such as public libraries and schools, are among the first places people go to access the Internet when they cannot access it at home. With 30% of the United States without a broadband connection at home, libraries and schools are essential for access to social services, job applications, and digital learning tools. These institutions, however, may not themselves have the capacity to meet the increasing demand for Internet access.
That can be a really big problem. With many states requiring online testing, schools need to have adequate bandwidth, so that networks do not crash at key moments. Some schools have to ration Internet access - while some students are testing, no one else is allowed to use the Internet. This means no video-streaming educational videos or remote learning classes while testing takes place. Educational opportunities shrink as students and teachers have to forego the most up-to-date online resources because of this bandwidth shortage.
The major barriers to high quality Internet access for community anchor institutions are cost and availability. National carriers like AT&T often do not provide the needed capacity at affordable rates. Municipal networks, however, are locally controlled and attuned to local needs. They treat community anchor institutions like a fundamental building block of society, not a profit center to be exploited.
72.2% of libraries help patrons access employment databases, and 58.8% of libraries face budget constraints when increasing their bandwidth.
63% of schools do not meet the ConnectED Current Goals for high speed connectivity which impacts nearly 40 million students in grades K-12.
-- Education SuperHighway’s Connecting America’s Students: Opportunities for Action
The federal E-rate program provides more than $2 billion in funding each year to support Internet access at public schools and libraries. The E-rate program, however, does not go far enough in helping these entities achieve high-capacity, reliable, and affordable Internet access. In too many cases, E-rate simply helps schools and libraries to afford connections priced at exorbitant levels from national carriers. Below, we detail the many benefits of local governments connecting their own community anchor institutions with self-provisioned networks - often called “institutional networks” or "I-Nets".
Learn more
Keep up to date with all things community broadband by subscribing to a once-per-week email with stories about community broadband networks.
Internet access is already crucial for community anchor institutions and will only become more important as society continues to incorporate technological advances into every aspect of life. Self-provisioning often results in higher capacity connections that are more reliable, and most importantly for local budgets, much more predictable in terms of future costs. Operating an institutional network, communities can plan years in advance for upgrades and have greater security in long term budgeting rather than worrying about the incumbent provider raising rates.
For example, Martin County in Florida had been leasing lines from Comcast to connect the schools and public buildings, but its 10-year franchise agreement was about to expire. With Comcast demanding a stunning price increase, Martin County instead built an underground fiber network with much more redundancy than Comcast offered. Compared to leasing lines, Martin County expects to save an estimated $30 million over the next twenty years. Now Martin County does not fear rate hikes or unexpected outages from Comcast’s network.
In talking with some schools that have transitioned from leased lines to operating their own network, some have reported that network management requires less staff time because the modern technology behind a wide-area network largely runs itself. If something goes wrong, staff have the information they need to diagnose and repair rather than having to wait on hold for a CenturyLink call center to begin investigating a problem.
This chart of five different school districts across the U.S shows some of the savings schools have experienced with municipal networks. The orange is the original provider’s exorbitant price for each Mbps per month. The blue is the price from the municipal network. The savings are stunning.
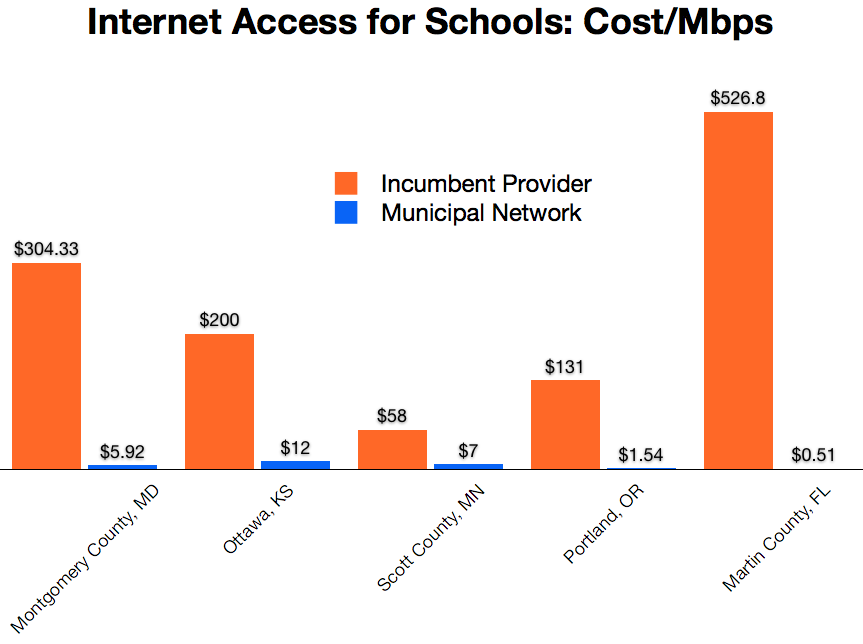
Sources for the graph: MuniNetworks Public Savings Fact Sheet and Breaking the Broadband Monopoly
For more information about costs and savings, dig into these examples of savings to community anchor institutions:
Libraries and schools have used the increased Internet capacity of some municipal networks to expand services and enhance their educational materials. Rural districts can use remote instruction via video-streaming to offer more foreign language and science classes. Communities have crafted innovative programs for students to explore how high-speed Internet access can be used in the classroom for more individualized and self-paced learning. These educational experiences cannot be achieved without high-capacity Internet access.

One of the many benefits of institutional networks is that communities can use the assets and knowledge from building those connections for economic development and other policy goals. For instance, when building the fiber to connect schools and libraries, smart communities install extra fiber that can be used to connect local businesses or form the backbone of a citywide network in the future if that becomes feasible. Many local governments have found that after building a high-speed institutional network, local businesses clamor for access as well.
Santa Monica is a great example of a community that started by self-provisioning community anchor institutions and has gone on to create many benefits for businesses and residents with both the savings and assets from the municipal network.
Without incurring any debt, the city built an expansive fiber network. They started by connecting municipal buildings and community anchor institutions with a $530,000 investment. Then, they expanded the network through grants for intelligent traffic systems and the savings from discontinuing expensive leased lines.
The city saved $400,000 the first year and $700,000 each subsequent year. With the extra fiber, Santa Monica provides better Internet access to local businesses and leases fiber to other service providers. The money from the municipal network is reinvested in the community, encouraging economic development. See our case study for more details.

These podcasts aim to be around 20 minutes long and feature issues related to libraries and schools.
| Episode | Title | Synopsis | Guests | Transcript |
| 79 | Don Means on Libraries and White Spaces | Explanation on TV white spaces wireless technology | Don Means | Transcript 79 |
| 71 | Education SuperHighway Wants Better Broadband for Schools | Education SuperHighway's approach to ensure better Internet connection to all schools and the role of community to achieve this goal | Evan Marwell | Transcript 71 |
| 46 | North Georgia School Brings Gig To Schools, Jobs to Region | The origin of the North Georgia Network and its economic and social impact on the region | Paul Belk | Transcript 46 |
| 43 | Carroll County Explains Many Benefits of County Owned Fiber | How Carroll County Public Network started and the benefit its community network provides | Gary Davis | Transcript 43 |
| 39 | Moultrie City Manager Discusses Origins of CNS Network in Georgia | The origin of CNS network in Georgia and the benefits of the network for local schools and community savings | Mike Scott | Transcript 39 |
Looking for even more information about libraries, schools, and Internet access? Here are archives of conferences, presentations, hearings, and other research.
Community-Based Broadband Solutions | Report PDF | January 2015 | The Executive Office of the President
The White House report features the savings to schools and libraries provided by locally controlled community networks.
Connecting America’s Students: Opportunities for Action | Report PDF | April 2014 | Education SuperHighway
This report examines E-rate spending and underscores the importance of Internet access in schools. The report attempts to answer why the connectivity gap persists and provide solutions to increase Internet access.
2013 Digital Inclusion Survey of Libraries | digitalinclusion.umd.edu | From the University of Maryland Funded by the Institute of Museum and Library Services
Each year, the University of Maryland releases a survey of digital information services that libraries across the U.S. offer. The reports highlight inequities in Internet access and the changing role of libraries.
Connected Communities in an Age of Digital Learning: a Vision for a 21st Century E-rate Program | Video Archive | February 27, 2014 | New America Foundation
This webcast concerned the modernization of the E-rate program and increasing Internet access at libraries and schools. Featured speakers included representatives from the Institute of Museum and Library Services, the U.S. Department of Education, New America’s Open Technology Institute, the Albemarle County (VA) Public Schools, and the Richland Library (SC).
Schools, Health & Libraries Broadband (SHLB) Coalition | www.shlb.org
The SHLB is a nonprofit organization formed in 2009 to support affordable, high-capacity broadband at anchor institutions. They develop and promote policies and programs that further connectivity in communities.
National Association of Telecommunications Officers and Advisors (NATOA) | www.natoa.org
A professional association of telecommunications officers and advisors that deal with communication policies and programs in local governments.
Photo of library computers courtesy of the Knight Foundation
Photo of library headquarters from the public domain
